The Biomedical Nano-Engineering (BNE) Laboratory led by Dr. Stefan Wilhelm has a broad interest in engineering biomaterials and colloidal nanomaterials for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, including cancer. Our areas of expertise include the design and synthesis of organic and inorganic nanomaterials with defined physicochemical properties (e.g., size, shape, surface chemistry, and optical/magnetic features).
Our group studies interactions between nanomaterials and biological systems from a whole organ/tissue perspective down to the cellular and bio-molecular level. This research will provide a foundation for the rational engineering of nanomaterials and nanomedicines with the ultimate goal of designing diagnostic and therapeutic nanomedicines that are safer and more effective.
Research Areas
Nanotechnology-biology (“nano-bio”) interactions
Using novel bioanalytical tools, we study nanoscale and nano-bio interactions at the single-particle and single-cell levels.
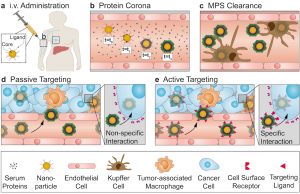
Nanoparticle surface engineering and nanotoxicity of biomaterials
Using innovative nanoparticle surface engineering strategies, we study nanoparticle pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and adverse effects.
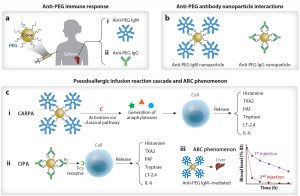
Cancer nanomedicine
Understanding nanoparticle interactions with the tumor microenvironment for safer and more effective cancer drug delivery.
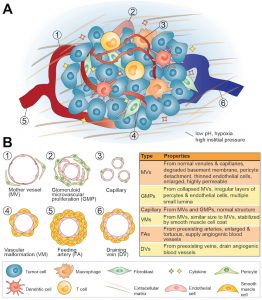
Immunoengineering and drug delivery
Targeted delivery of peptides, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids to immune cells for immunotherapy and vaccine applications.

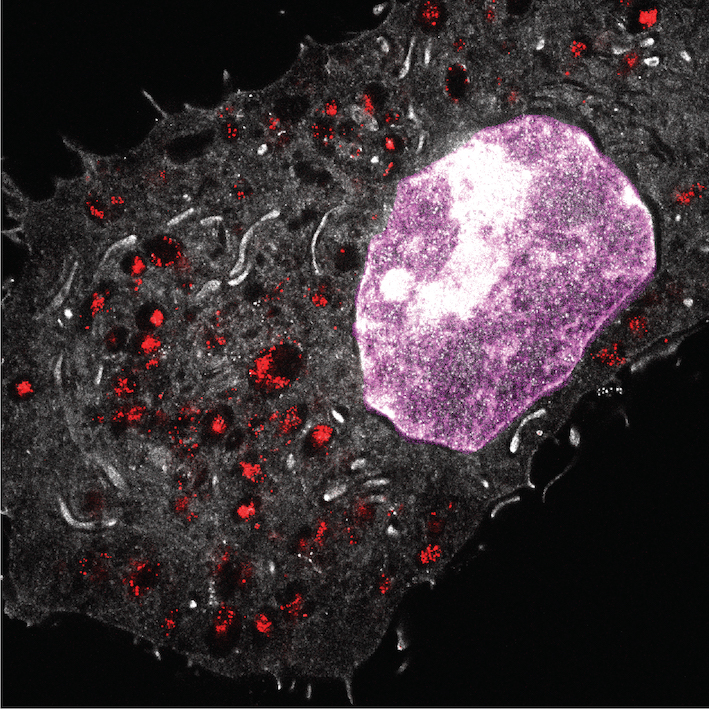
Super-resolution imaging
Expansion microscopy of cells, tissues, and organs to elucidate nanoparticle transport and fate.
Translational Research
Student-led commercialization projects, including ClotShield, a medical device aimed at automatic blood testing to prevent Pulmonary Embolism.

Research Environment
Our laboratory is located in the state-of-the-art biomedical research facility Gallogly Hall (opened in Fall 2019). We are a member of the NCI-designated Stephenson Cancer Center and the Harold Hamm Diabetes Center with access to unique research facilities and collaborators at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center campus.


Laboratory Instrumentation and Equipment
- Agilent Cary 5000 UV-Vis-NIR Spectrophotometer
- Agilent 1260 Infinity II HPLC
- Andor BC43 Benchtop Microscope
- Azure Biosystems 600 UV-Vis-NIR Imaging System
- Beckman Coulter Optima MAX XP Ultracentrifuge
- BioTek Synergy Neo2 Multi-Mode Plate Reader
- Branson 3800 Ultrasonic Cleaner
- Büchi Rotavap R-100
- Chemglass Schlenk Line
- Cytek Nothern Lights Flow Cytometer
- DeNovix CellDrop BF Cell Counter
- DeNoxix D11+ Spectrophotometer
- Eppendorf 5427R and 5910R Centrifuges
- Eppendorf Galaxy 170 S and CellXpert Cell Incubators
- Freezers (-20°C) and Fridges (4°C)
- Harrick Basic Plasma Cleaner
- Horiba PTI Quanta Master 8000 Fluorometer
- Horiba ViewSizer 3000 Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis System
- Hoshizaki Ice Maker
- Kent Scientific Low-Flow Electronic Rodent Anesthesia System
- Kewaunee Scientific Corporation Fume Hoods
- Keyence BZ-X800 Automated Fluorescence Microscope
- Labconco Logic Plus Biological Safety Cabinet and FreeZone Freeze Dryer
- Malvern ZetaSizer Nano ZS
- Mettler Toledo S220 pH Meter
- MVE Cryosystem 6000 Cell Storage
- Miltenyi Biotec gentleMACS Octo Tissue Dissociator
- Miltenyi Biotec autoMACS Cell Separator
- Nova Automated Water Bath
- Olympus CKX53 Optical Microscope
- PerkinElmer IVIS SpectrumCT
- PerkinElmer NexION 2000 ICP-MS
- PHCBI Minus 80°C Freezer
- Purist Pro UV Ultrapure Water System
- Repligen KrosFlo KR2i Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF)
- Sartorius Analytical and Precision Balances
- Steris AMSCO 250 LS Autoclaves
- Thermo Heraeus Multifuge X3R and Fresco 21 Centrifuges
- Tofwerk icpTOF R with Quantistar Microdroplet System
- Wyatt DynaPro Plate Reader III
- Wyatt FFF-MALS/DLS
- Zeiss LSM 780 Microscope
Research Collaborators
- Prof. Adam Asch (MD, Stephenson Cancer Center, Department of Hematology/Oncology)
- Prof. Resham Bhattacharya (PhD, Health Sciences Center, Department of Obsterics and Gynecology)
- Prof. Paul DeAngelis (PhD, Health Sciences Center, Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)
- Prof. William Hildebrand (PhD, Health Sciences Center, Department of Microbiology & Immunology)
- Prof. Priyabrata Mukherjee (PhD, Health Sciences Center, Department of Pathology)
- Prof. Rakhi Rajan (PhD, OU Chemistry/Biochemistry)
- Prof. Wajeeha Razaq (MD, Stephenson Cancer Center, Department of Hematology/Oncology – Breast Cancer)
- Prof. Takemi Tanaka (PhD, Health Sciences Center, Department of Pathology – Breast Cancer)
- Prof. Yan Daniel Zhao (PhD, Health Sciences Center, Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiology)
Funding Sources
Our research is supported by the following agencies:






